- AI Pulse
- Posts
- 🤯 OpenAI Reclaimed Its Lost AI Brainpower?
🤯 OpenAI Reclaimed Its Lost AI Brainpower?
Why top AI researchers walked away and why they just came back to OpenAI.

Hello There!
OpenAI just pulled off a rare talent reversal as senior researchers who once left to build their own lab quietly returned, and for professionals this is a reminder that even in AI the safest seat is still close to power. OpenAI also locked in massive new compute capacity with Cerebras to make AI faster and more responsive, which means your tools may soon feel snappier while your expectations quietly rise with them. And as a lip syncing humanoid robot learns to speak and sing by watching itself and humans, professionals should brace for a future where machines communicate more naturally and meetings get a little less comfortable.
Here's what's making headlines in the world of AI and innovation today.
In today’s AI Pulse
📊 Deel – 2026 HR trends every leader must know.
🧠 The Code – Tech insights engineers read weekly.
📰 Beehiiv – Launch a revenue-ready newsletter in minutes, no code needed.
🧠 OpenAI - Reclaims Lost AI Brainpower Team
⚡ OpenAI - Taps Cerebras For Faster Computer
🤖 Lip Sync - Robot Learns to Sing
⚡ Quick Hits – IN AI TODAY
🛠️ Tool to Sharpen Your Skills –🎓 AIGPE® Certified Six Sigma Green Belt
The coming years won’t just transform technology; they’ll reshape your home, your family life, and the control you have online.
Hiring in 8 countries shouldn't require 8 different processes
This guide from Deel breaks down how to build one global hiring system. You’ll learn about assessment frameworks that scale, how to do headcount planning across regions, and even intake processes that work everywhere. As HR pros know, hiring in one country is hard enough. So let this free global hiring guide give you the tools you need to avoid global hiring headaches.
Find out why 100K+ engineers read The Code twice a week.
That engineer who always knows what's next? This is their secret.
Here's how you can get ahead too:
Sign up for The Code - tech newsletter read by 100K+ engineers
Get latest tech news, top research papers & resources
Become 10X more valuable
We’re running a super short survey to see if our newsletter ads are being noticed. It takes about 20 seconds and there's just a few easy questions.
Your feedback helps us make smarter, better ads.
🧠The Pulse
Several key leaders from former OpenAI CTO Mira Murati’s Thinking Machines Lab — including co-founders Barret Zoph and Luke Metz plus researcher Sam Schoenholz — have left the startup and are rejoining OpenAI, marking one of the most dramatic talent shifts in the AI talent war this year. Leadership changes are now unfolding.
📌The Download
Major leadership returns – OpenAI’s CEO of Applications Fidji Simo announced on X that Barret Zoph, Luke Metz and Sam Schoenholz would be returning to OpenAI after previously leaving to help start Thinking Machines Lab.
Startup upheaval – Mira Murati’s startup confirmed the departure of Zoph, replacing him with veteran AI leader Soumith Chintala as its new CTO, signalling internal shifts.
Talent war context – This mass return comes amid a broader struggle for elite AI researchers, with multiple departures at Thinking Machines and industry offers from firms like Meta.
Industry signal – The moves highlight how even well-funded AI startups face challenges retaining founders and senior researchers when legacy players like OpenAI attempt to re-attract top technical talent.
💡What This Means for You
If you collaborate with or monitor AI innovation trends, this shift underscores how talent concentration remains critical in shaping research priorities and product roadmaps. For professionals, understanding how personnel flows influence competitive advantage and strategic direction can inform vendor selection, benchmarking, hiring decisions, and investment insights across high-growth AI initiatives.
🧠The Pulse
To speed up ChatGPT and future models, OpenAI signed a multi‑year deal with Cerebras to add 750 megawatts of low‑latency AI compute. Cerebras’ wafer‑scale engines pack memory and bandwidth on a single chip, promising faster responses and scalable infrastructure through 2028.
📌The Download
Massive capacity – Cerebras will provide up to 750 MW of AI compute to OpenAI under a long‑term agreement. The compute will be hosted in data centres using Cerebras’ wafer‑scale engines, each containing a whole silicon wafer to maximise bandwidth.
Low‑latency design – By integrating memory and compute on a single chip, Cerebras systems dramatically reduce data transfer delays. OpenAI says the capacity will deliver faster responses for real‑time applications, improving user experience and enabling new AI services.
Scale through 2028 – The new compute will come online gradually through 2028, ensuring a steady ramp‑up of resources. This approach gives OpenAI flexibility to deploy and optimise models without overwhelming existing infrastructure.
Diversifying suppliers – Partnering with Cerebras diversifies OpenAI’s hardware sources beyond established chip makers, potentially easing supply constraints and fostering competition among AI hardware vendors.
💡What This Means for You
Expect AI services to get faster as novel chips reduce latency. For professionals relying on AI tools, this could mean smoother interactions and more responsive assistants. Organisations planning new AI products should watch hardware innovations and evaluate how emerging chip architectures might improve performance and cost efficiency.
🧠The Pulse
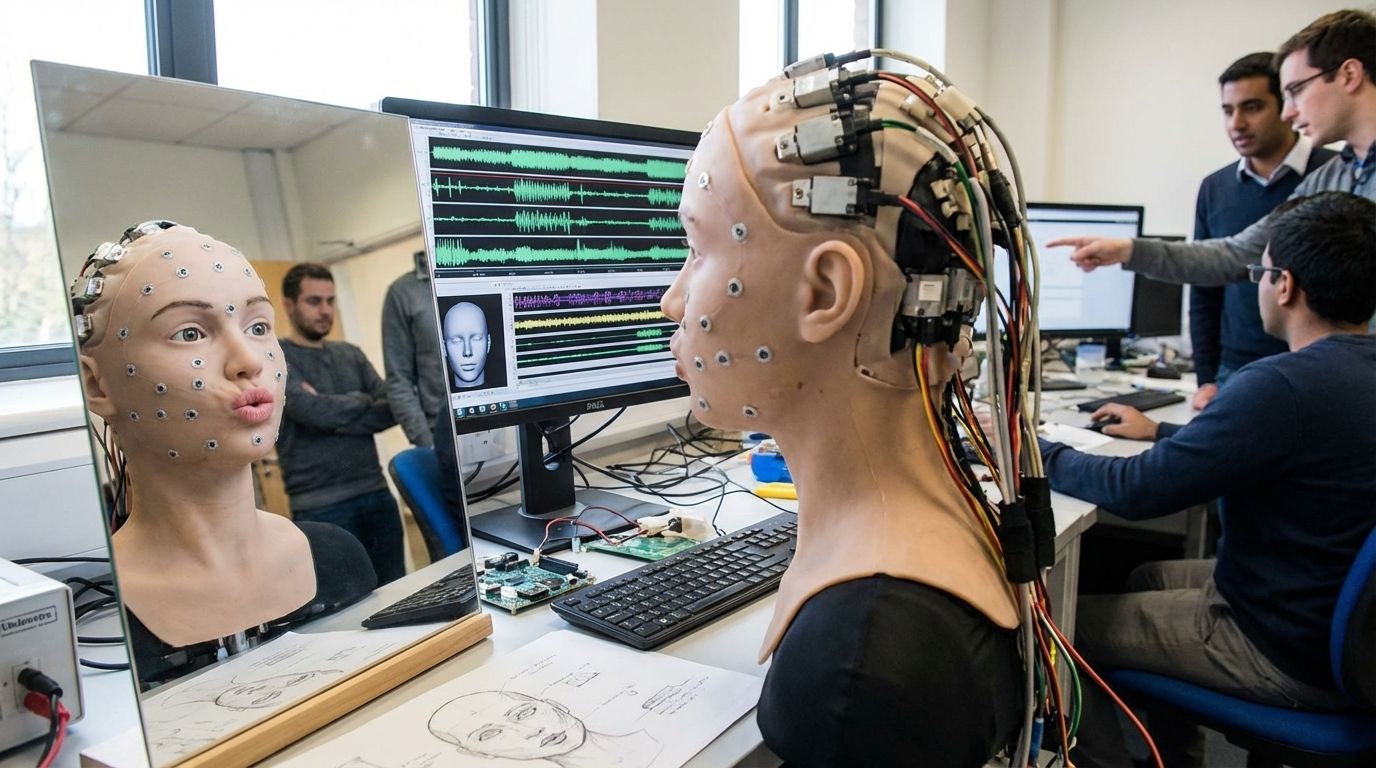
Columbia University engineers built a humanoid robot that learned to synchronize lip motions with speech by watching itself and humans. Using a flexible face with 26 motors and a vision‑to‑action model, the robot taught itself to speak and sing, signalling a leap in expressive robotics and human–machine interaction with empathy.
📌The Download
Mirror and motors – The robot first learned to control its own 26 facial motors by watching its reflection in a mirror. Through thousands of random expressions, it discovered the relationships between motor movements and facial shapes using a vision‑to‑action language model.
Learning from humans – After mastering its own face, the robot studied hours of human speech and singing videos on YouTube. It associated audio patterns with lip shapes across multiple languages, enabling synchronized mouth movements for talking and singing.
Crossing the uncanny valley – The researchers say realistic lip motion is crucial because humans notice small mistakes. By learning through observation instead of preset rules, the robot reduces the eerie effect of stiff, puppet‑like expressions and could help future robots communicate naturally.
Towards expressive AI – The team plans to integrate lip synchronization with conversational AI to add depth to interactions. They argue that facial expression is the missing link for humanoid robots and that more than one billion machines could soon need lifelike faces.
💡What This Means for You
Lifelike lip motion could make service and social robots more engaging. Professionals may soon work with robots capable of expressing emotion through facial cues and synchronised speech. Prepare to interact with machines that communicate more naturally, raising expectations for ethical design, emotional intelligence and user training in client‑facing roles too.
IN AI TODAY - QUICK HITS
⚡Quick Hits (60‑Second News Sprint)
Short, sharp updates to keep your finger on the AI pulse.
Publishers Join Google AI Copyright Lawsuit: Textbook publishers including Hachette and Cengage sought to join existing lawsuits against Google, alleging the company’s AI training uses copyrighted books without permission. The plaintiffs argue that Google’s generative models were built on “one of the most egregious” infringements, and they aim to help resolve evidentiary and legal issues.
Physical AI Rising: Physical AI stole the spotlight at CES 2026 as robots left computer screens behind. Boston Dynamics’ production‑ready Atlas, Hyundai’s plan to build 30,000 humanoids per year, LG’s domestic assistance robots and Nvidia’s Alpamayo self‑driving intelligence signaled that autonomous machines are moving quickly from demonstrations to deployment for workers globally soon.
TOOL TO SHARPEN YOUR SKILLS
📈Improve Processes. Drive Results. Get Certified.
Learn to design complete project schedules using ChatGPT. Build timelines, milestones, dependencies, and Gantt charts with step-by-step guidance.
That’s it for today’s AI Pulse!We’d love your feedback, what did you think of today’s issue? Your thoughts help us shape better, sharper updates every week. |
🙌 About Us
AI Pulse is the official newsletter of AIGPE®. Our mission: help professionals master Lean, Six Sigma, Project Management, and now AI, so you can deliver breakthroughs that stick.
Love this edition? Share it with one colleague and multiply the impact.
Have feedback? Hit reply, we read every note.
See you next week,
Team AIGPE®